muscle that extends the elbow
 Muscles of the Elbow and Forearm - dummies
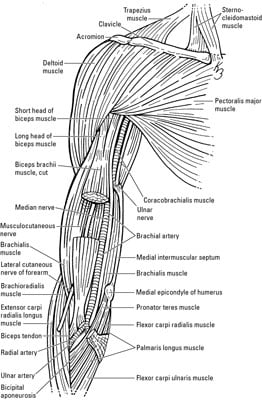
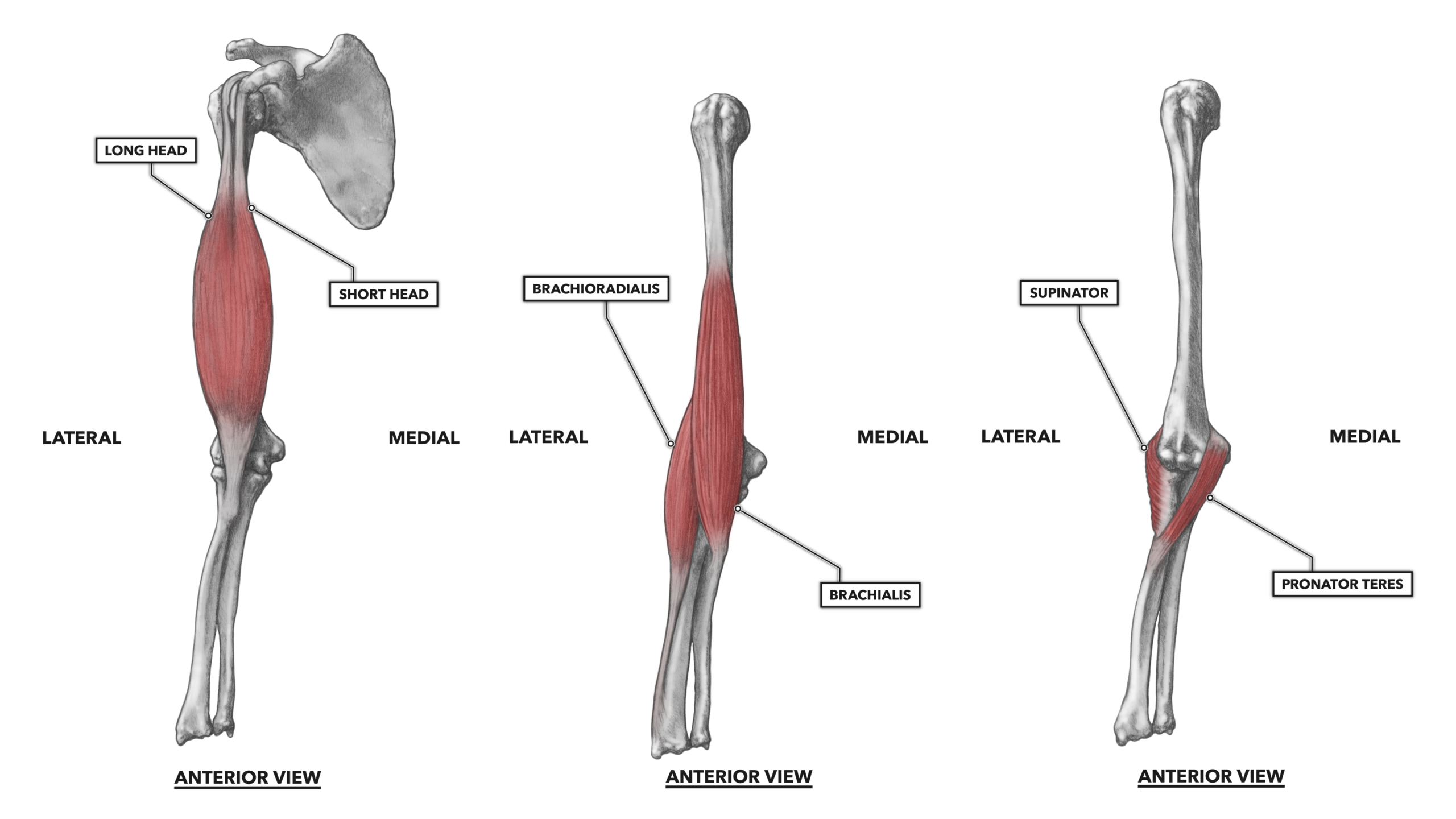
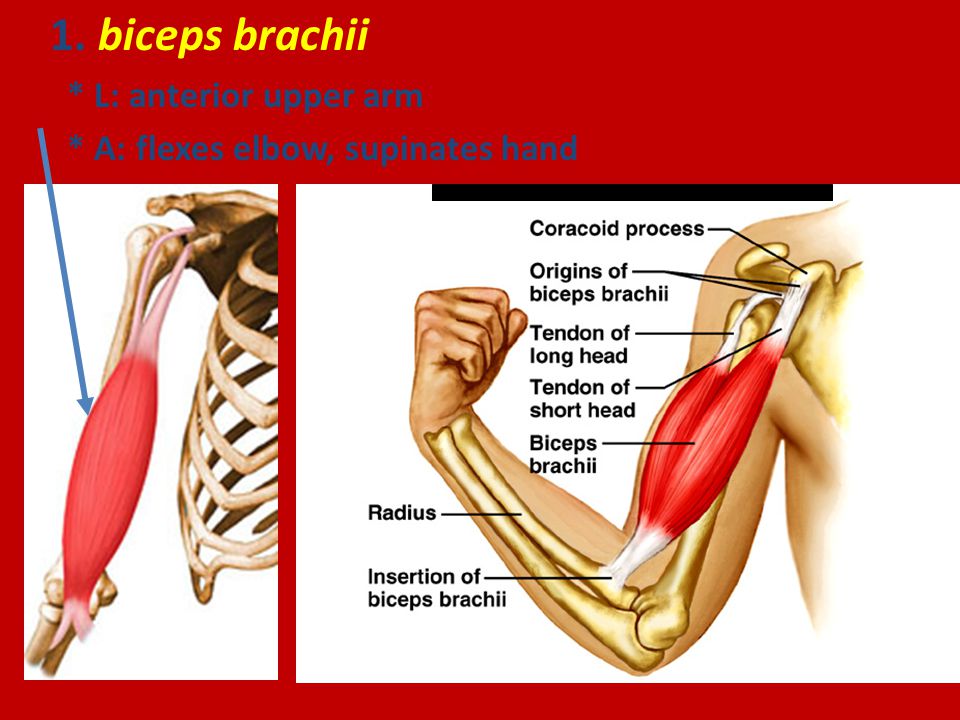
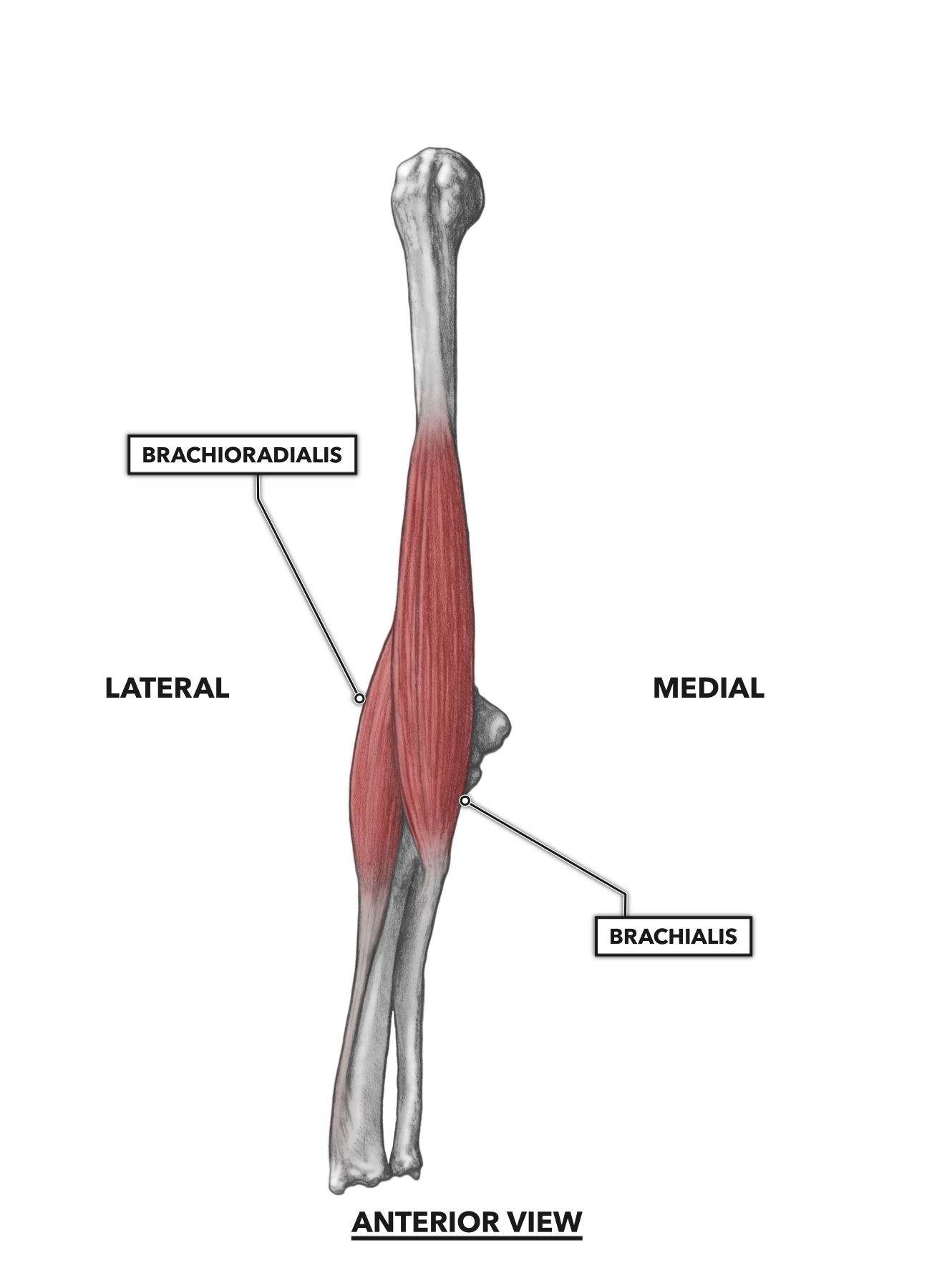
Muscles of the Elbow and Forearm - dummiesAdvert Muscles of the elbow The elbow is a synovial hinge joint located between the upper arm and the forearm. It is made up of three bones: the humerus on the upper arm and the ulna and the radius on the lower arm. Like all other hinge joints, the elbow allows movement on a plane, namely, bending and extension of the forearm relative to the upper arm. However, the elbow also allows the wrist to rotate the radio around the ulna. The elbow muscles cooperate to make the many movements in the elbow joint, giving both strength and flexibility to the arm. Additional ResourcesAnatomy Explorer Current Change View AngleToggle Anatomy SystemAnatomy TermDisplayed on other pageJoin our Newsletter and receive our free ebook: Guide to Master's in Anatomy StudyThank you for subscribe! Please check your email to confirm your subscription. There was an error in sending your subscription. Please try again. We hate spam as much as you do. Subscribe at any time. There are seven main muscles present in the elbow that flex it, extend it or turn the forearm. Another nine muscles cross the elbow to act on the wrist and the joints of the hand. These muscles can be grouped extensively into the flexor and ancestor groups. The flexor group - including brachialis, biceps brachii and brachioradialis - bend the arm decreasing the angle between the forearm and the upper arm. Brachialis is the primary bend of the elbow and is mainly found in the upper arm between the humerus and the ulna. Surface to brachialis is the long muscle of brachii biceps that runs prior to the humerus of the escapula to the radio. The biceps work mainly as a bend in the elbow, but it is also able to supthe the forearm and turn the palm of the previous hand. Although it is mainly in the forearm, brachioradialis is the third bending muscle of the elbow, running from the distal end of the humerus to the distal end of the radio. Two muscles - the brachii triceps and the ancon - act as the forearm extenders. The triceps brachii is a long muscle that runs after the humerus of the escapula to the olecranon of the ulna. The ancon is a much smaller muscle that begins at the distal end of the humerus near the elbow and ends in the olecranon. Working together, these two muscles increase the angle between the humerus and the ulna and the radio, straightening the arm until the olecranon is blocked in the olecranon pit of the humerus to full extent. The rotation of the forearm is made by two muscles that cross the elbow: the pronator teres and the supinator. The pronator teres crosses the elbow at an oblique angle from the medial epicondillium of the humerus to its insertion into the radio. When contracted, the pronator teres rotates the radio and the forearm medially so that the palm faces to the back of the body. Its antagonist, the suppander, crosses the elbow obliquely at a straight angle to the pronator teres and connects the lateral epicondylium of the humerus to the radio. The supinator's traction rotates the radio and the forearm laterally so that the palm faces the previous body. (adsbygoogle = window.adsbygoogle TENTED []).push({}); Nine more muscles of the forearm cross the elbow to move the wrist and fingers of the hand. The flexor group - including the flexor carpi radialis, flexor carpi ulnaris, palmaris longus, and flexor digitorum superficialis - have their origins in the medial epicondyle of the humerus and run along the forearm before the palm of the hand and fingers. These muscles contract to flex their fingers as a fist and flex the wrist to move the hand closer to the previous forearm. The extender group - including the carpi radialis longus extender, carpi radialis brevis extender, and digitorum extender - have their origins in the lateral epicondile of the humerus and run through the forearm post to the back of the hand and fingers. The traction of the extended muscles extends the hand and fingers to open a tight hand and extend the wrist to the back of the forearm. With so many muscles that originate or are inserted near the elbow, perhaps it is not surprising that the elbow is a common site for the injury. A common lesion is lateral epicondylitis (or tennis elbow), pain of the forearm's extended muscles attached to the lateral epicondile of the humerus. The repetitive and vigorous contraction of muscles (such as hitting many back strokes in tennis) causes tension in tendentious muscle attachments, which leads to pain. Avoiding the repetitive effort of these muscles usually brings recovery. Innerbody Research is the largest home health and well-being guide online, helping more than a million visitors every month learn about health products and services. Our mission is to provide science-based objective advice to help you make more informed decisions. GUIDESREVIEWSABOUT

Level 3 (68) Exercise and Fitness Knowledge: The elbow joint, radioulnar joint and wrist - Amac Training

Elbow Arm Anatomy
elbow tendon Archives - The Handcare Blog

G. Muscles of the Arm * move the forearm (elbow). - ppt video online download
CrossFit | Elbow Musculature, Part 1: Anterior Flexors
Muscle Identification

Elbow Arm Anatomy
G. Muscles of the Arm * move the forearm (elbow). - ppt video online download

Triceps / Biceps Muscle Rupture

Level 3 (68) Exercise and Fitness Knowledge: The elbow joint, radioulnar joint and wrist - Amac Training
CrossFit | Elbow Musculature, Part 1: Anterior Flexors

Muscles of the Pectoral Girdle and Upper Limbs | Anatomy and Physiology I
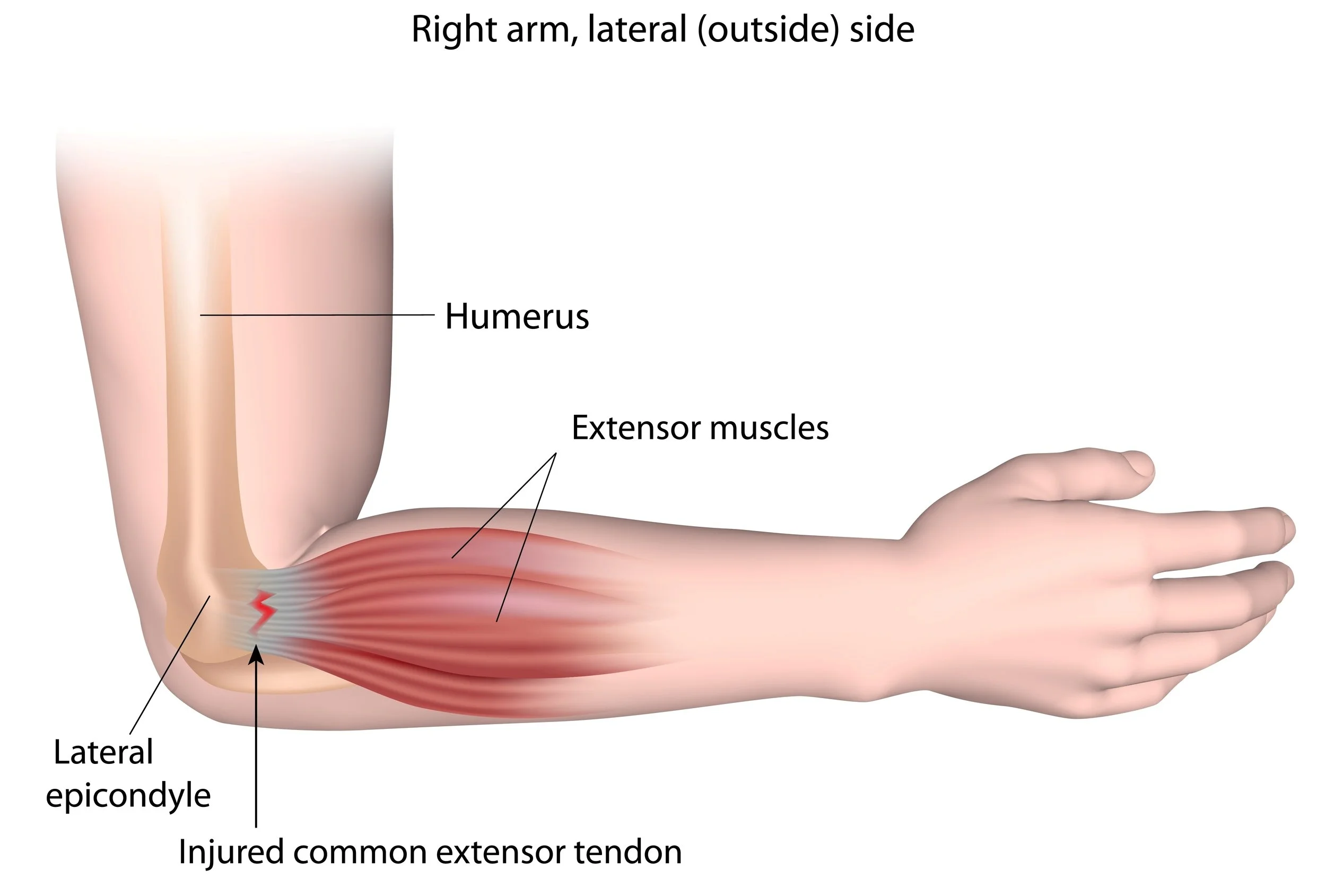
Tennis Elbow - Lateral Epicondylitis - Raleigh Hand Surgery — Joseph J. Schreiber, MD
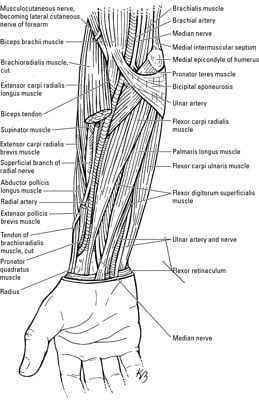
Muscles of the Elbow and Forearm - dummies
General Principles - Skeletal Muscle Anatomy
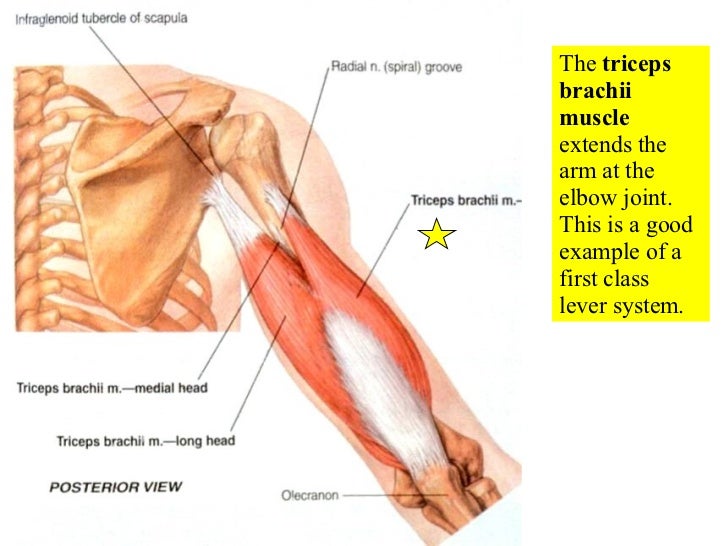
12 Appendicular Muscles
Body Anatomy: Upper Extremity Muscles | The Hand Society
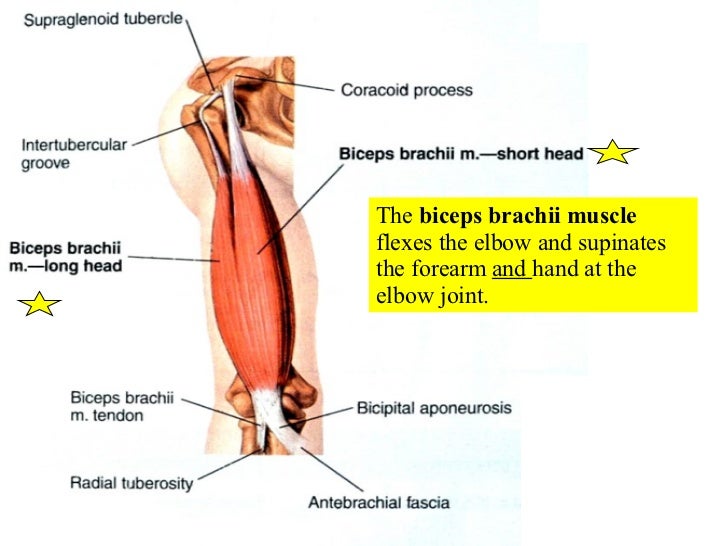
12 Appendicular Muscles
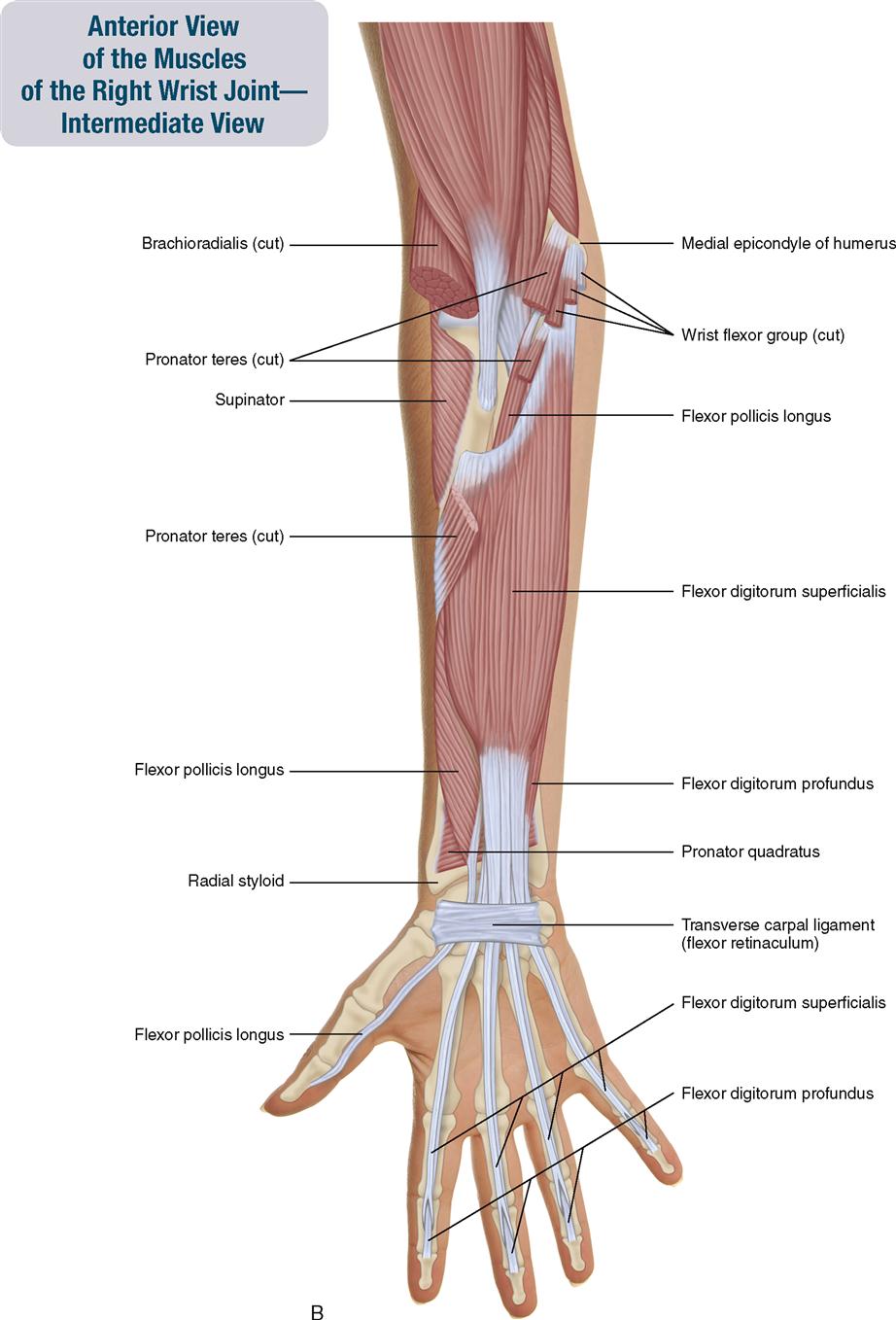
7. Muscles of the Forearm and Hand | Musculoskeletal Key
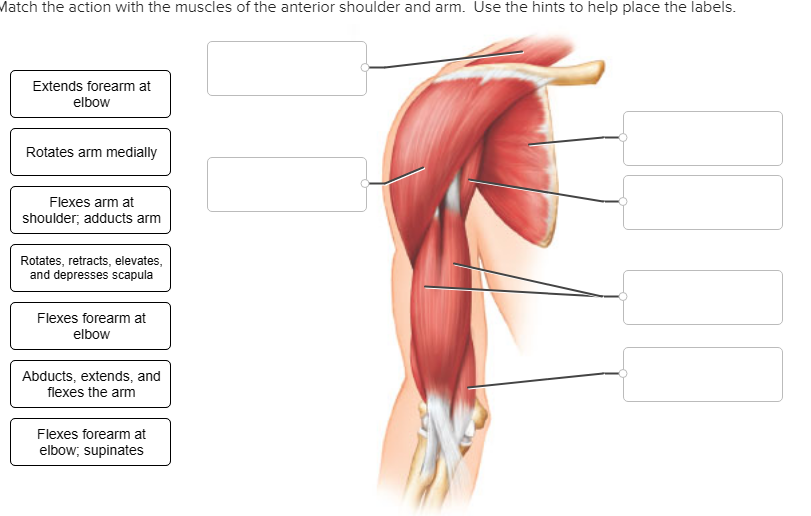
Solved: Match The Action With The Muscles Of The Anterior ... | Chegg.com

Elbow Tendons Anatomy - Anatomy Drawing Diagram

Muscles of the Upper Limb | Boundless Anatomy and Physiology
Muscles of the Shoulder & Arm - Kirsten's Anatomy Website

human muscle system | Functions, Diagram, & Facts | Britannica

Elbow Joints-Muscles Flashcards | Quizlet
Body Anatomy: Upper Extremity Tendons | The Hand Society
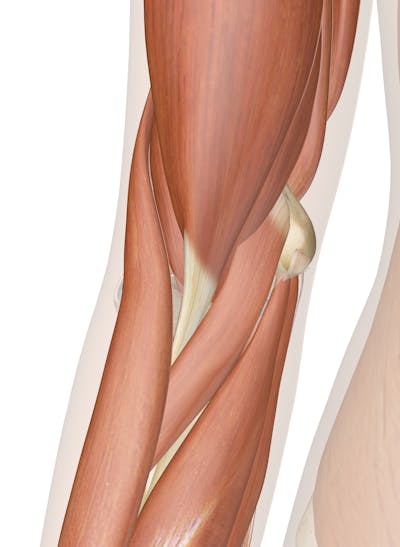
Muscles of the Elbow | Interactive Anatomy Guide
Elbow Muscles Anatomy, Diagram & Function | Body Maps
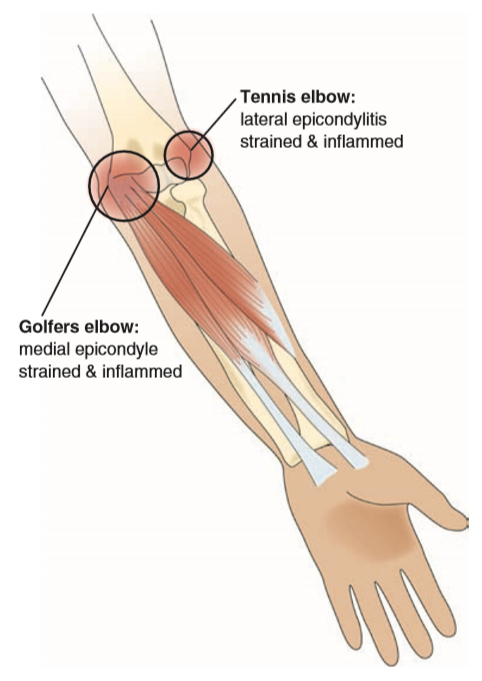
Hand, Wrist, Forearm, and Elbow muscle imbalances - Strong Links Fitness

arm | Definition, Bones, Muscles, & Facts | Britannica
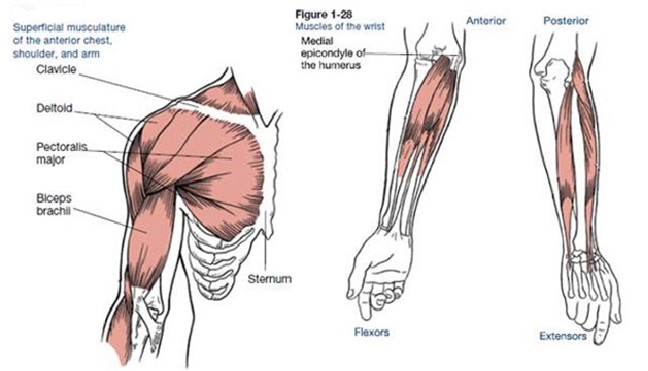
Muscles That Move the Arm

Elbow Joint Muscles - TeachPE.com

Level 3 (68) Exercise and Fitness Knowledge: The elbow joint, radioulnar joint and wrist - Amac Training
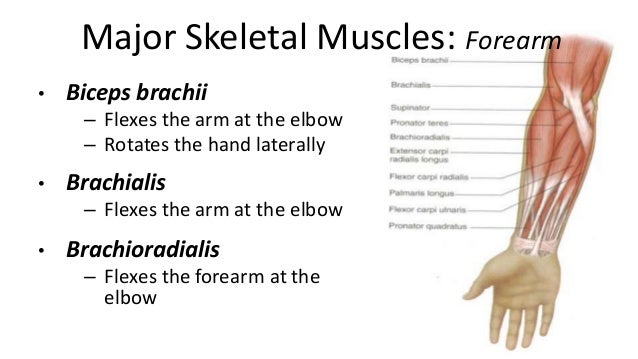
Muscular system

Muscles – Advanced Anatomy 2nd. Ed.
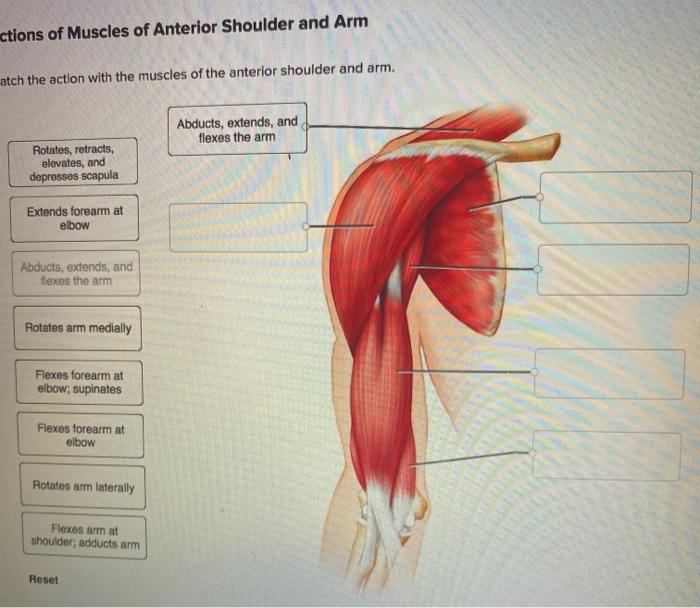
Solved: Actions Of Muscles Of Anterior Shoulder And Arm At... | Chegg.com

Elbow Joint Muscles - TeachPE.com

Elbow Flexion - an overview | ScienceDirect Topics
/elbowpainfinal-01-5c4e4272c9e77c00014afb3b.png)
Elbow Pain: Causes, Treatment, and When to See a Doctor
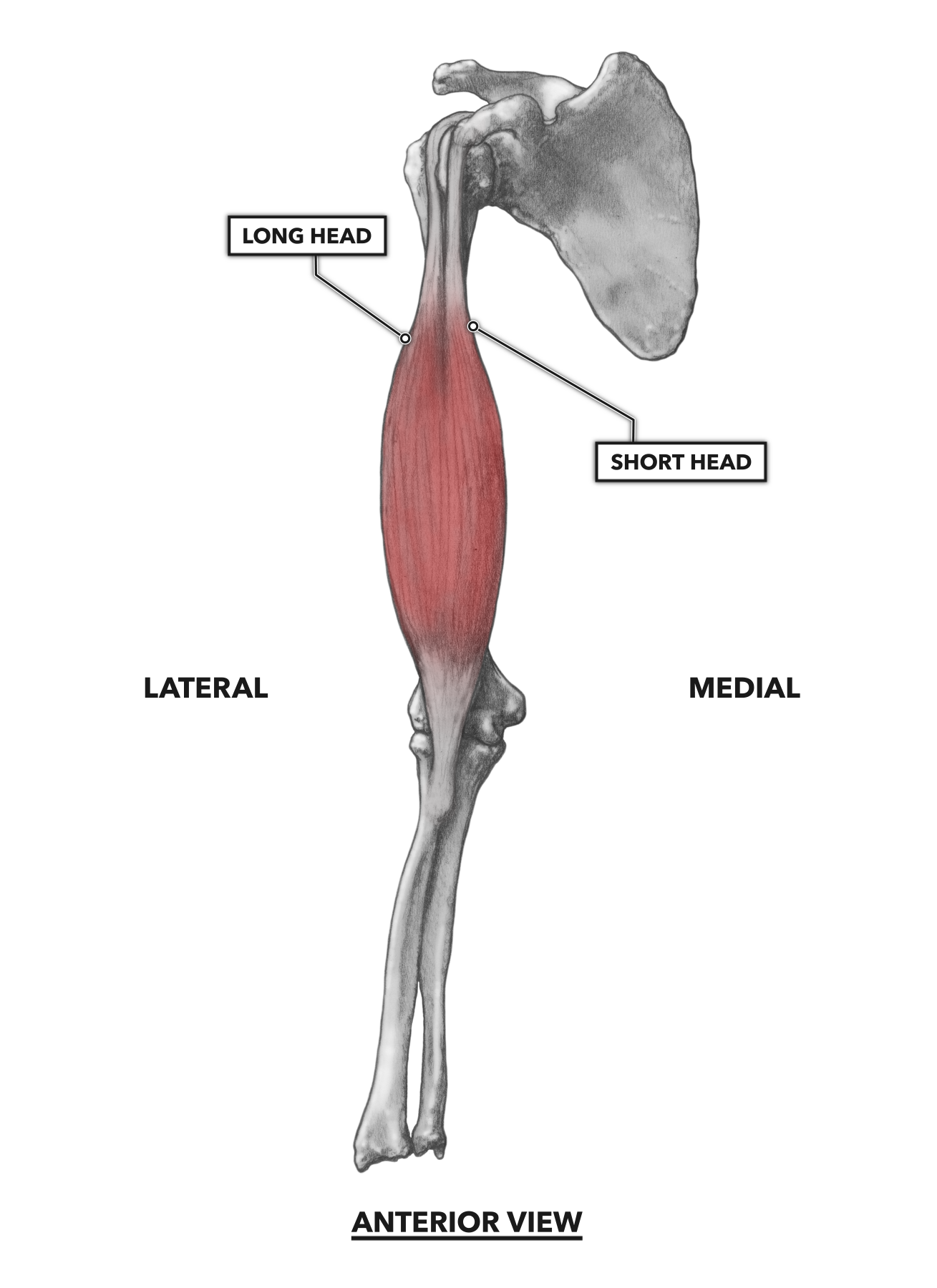
CrossFit | Elbow Musculature, Part 1: Anterior Flexors
Posting Komentar untuk "muscle that extends the elbow"